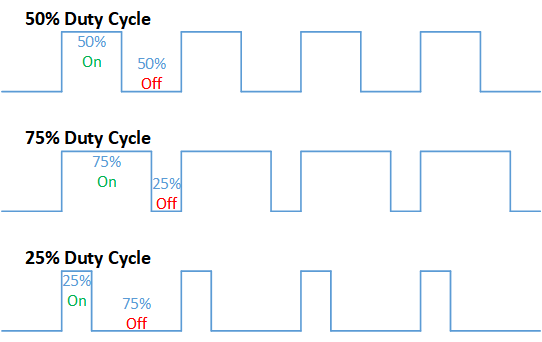
The technique of controlling motor speed using PWM signals is very common. This circuit uses similar PWM technique to control motor speed and uses IC 555 to generate PWM signals. For those who are not aware, PWM or Pulse Width modulation , is a modulation technique in where the width of the output pulse varies with with respect to time. This therefore changes the duty cycle of the wave which in turn modifies on and off time of this PWM signal. Lets see how this DC motor speed control circuit works.
WORKING OF DC MOTOR SPEED CONTROL CIRCUIT:
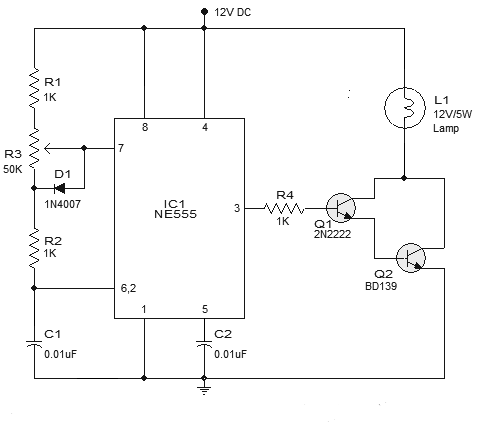
The heart of this circuit is an Astable multivibrator built out of IC 555. This multivibrator produces a series of square wave pulses as output of fixed frequency. Generally the output frequency of the Astable multivibrator depends on the Resistors and Capacitors attached to it.
A 555 astable multivibrator output duty cycle can never go down below 50%. In order to achieve PWM signal in output we should be able to modify the duty cycle as per our desire. This is where the components D2,D1, RV2 comes into picture.
Working of this astable multivibrator depends on the resistors and capacitor used with pin 7, pin 6 and pin 2. When the circuit is powered ON capacitor C1 charges via resistor R1 and RV2. But if you notice the circuit the current from R1 can pass through only one terminal of our variable resistor since D2 is reverse biased.
Hence D1 allows current to flow through it and RV2 exhibits some resistance to the current which depends on the position of the pot. When the capacitor is charging output of IC 555 will be in high state.
Once the capacitor charges up to 2/3 vcc, internal discharge transistor which connects to pin 7 goes high. Now output of IC 555 will goes to low. This forces the capacitor to discharge through RV2. But this time the discharging current goes through diode D2 since D1 is reverse biased.
The resistance exhibited by RV2 to discharging current will be different from what exhibited to charging current of capacitor. Therefore the discharge time of capacitor will be different from charging time.
This varied charging and discharging time will modify the width of our output pulse. This results in a PWM output signal in the output. When RV2 is set up in a way it exhibits very high resistance to charging current coming from D1, output pulse will have longer ON time.
On the other hand this will leave low resistance path for discharge current going out via D2, therefore Capacitor discharges quickly making the OFF time shorter. Thus we will get a high duty cycle PWM pulse. If we reverse the resistance, low time will longer and high time will be much shorter comparatively. This will allow us to get PWM signal much lower than 50%.
CALCULATION:
We can perform a simple calculation to understand this better.
Charging time or ON time = 0.693 ( R1 + RV1 ) C2
Discharge time or OFF time = 0.693 x RV2 x C2
If the variable resistor was set to exhibit 10k resistance between terminal 1 and 2. Then this will be the resistance to charging path by RV1. At this point terminal 2 and 3 in RV2 will exhibit 90k resistance to discharge path. Substituting the values in above formula
ON time = 0.693 ( 2.2k + 10k ) 1uF
= 8.5ms
OFF time = 0.693 x 90k x 1uF
= 62.37 ms
T = ON time + OFF time = 8.5ms + 62.37ms = 70.87ms
Duty cycle = 8.5ms / 70.87ms = 12%
Now if we alter the RV1 to make the resistance in terminal 1 and 2 as 90k and terminal 2 and 3 as 10k. Our duty cycle changes vastly
ON time = 0.693 ( 2.2k + 90k )1uF
= 63.9ms
OFF time = 0.693 x 10k x 1uF
= 6.93ms
T = 63.9ms + 6.93ms = 70.83ms
Duty cycle = 90%
From the above calculation you can see that providing different charging and discharging path with different resistance will enable us to produce PWM pulse from IC 555. Modifying the resistance value of RV1 between its terminals will modify the duty cycle.
MOTOR DRIVER:
The next stage of this circuit is quite. The output of the IC 555 is pretty low to drive a motor that can consume 500mA. Therefore a transistor is used as a switch here. The PWM signal is will drive the base of transistor Q1. This drives the motor according to the incoming signal from the output of the 555 IC. When the duty cycle of the PWM signal is high then the speed of the motor will be high and vice versa. Diode D3 is used to arrest the reverse current from motor when it is turned off.
PCB DESIGN:
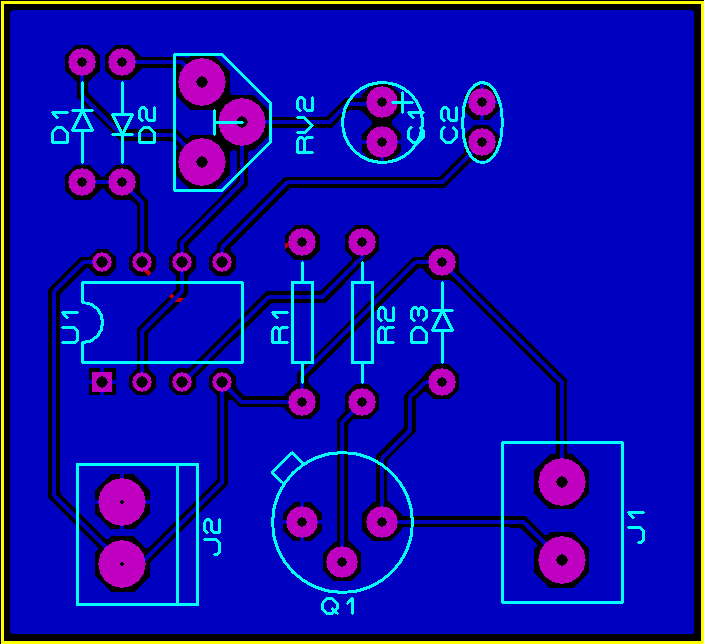 J1 the two pin screw terminal that connects DC motor to the circuit and J2 to connect power supply to the circuit. You can download the gerber files from below button.
J1 the two pin screw terminal that connects DC motor to the circuit and J2 to connect power supply to the circuit. You can download the gerber files from below button.
VIDEO EXPLANATION:
This circuit is simple to implement and very efficient in working.This will be a great project to do for Electronics hobbyist and students. If you have any questions leave them in the comment box below.

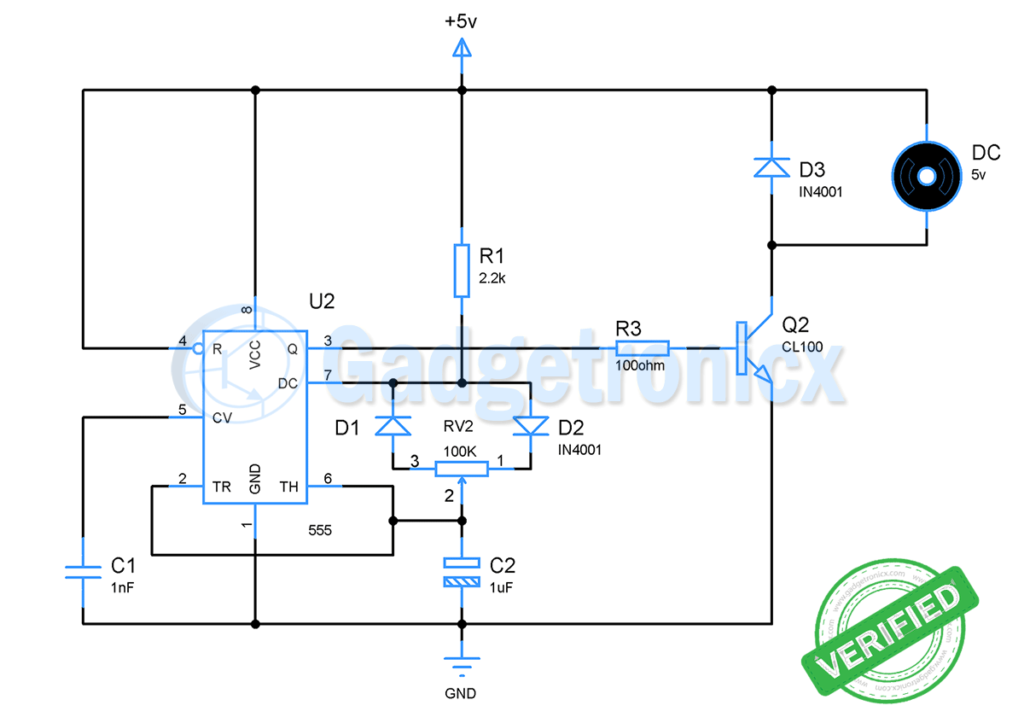

Is it necessary to use D1 D2?
Sg,
The Diodes D1 and D2 is used to route the charge and discharge currents to the ends of the POT R1. You can skip these two diodes and use just POT R1
I MADE THIS CIRCUIT AND IT WORKED PERFECTLY but at first i didnot understand how to connect motor then i just connect two 9v battery , one to power the ic and the other for motor ( 3v)
the technique is to connect the +ve of 2nd battery to vm and the -ve to pin 1 of ic or -ve of 1st battery
Zain,
Glad you figured it out, bravo. You could share your work with us if you worked on any specific applications using this circuit.
Hey, can you explain what is the function of c1 and c2
Jenn,
C2 was used to remove the ripples or noise in the circuit. Whereas C1 was a part of the timing element along with R1 and R2. This decides the frequency and width of the output pulse.
Hi, can you please explain what is the function of transistor Q1?
Prakhar,
The 555 cannot provide enough current to drive the motor by itself so we are using transistor to drive the motor.
What is the function of transistor Q1?
Hi, can I use relay instead of DPDT switch.(I dont have DPDT switch) and can I use 2 source in circuit
Thank you
Asli,
DPDT switch is just used to change the direction of your motor, so you can use this circuit eliminating the DPDT switch.
Hi, i m not really understand abt the way to connect the voltage to the motor, where is the return path of this voltage? Can u pls explain to me? tq very much
Bernice,
In the above schematic motor is switched by using transistor i believe you are familiar with transistor switches if not refer this Trasnistor switches tutorial link to learn about it. The motor was connected the V+ and GND paths using DPDT switch to control the direction of rotation. Hope this cleared the doubt.
ok.. i ll try to understand It is ok if i use the same voltage source for both Vm and the V needed by the ic?
Bernice,
Yes you can but make sure your source can provide sufficient current for both motor and IC , usually it does.
what is the function of 3 diodes in this circuit. plz explain each??
The Diodes D1 and D2 is used to route the charge and discharge currents to the ends of the POT R1. And D3 is meant to protect the circuit from the reverse current which flows when the motor is turned off.
Hi,
I build your speed controller using the 555 ic and it works but the 33 ohm resistance gets very hot, is that ok ?.
And I conected a jumper from the 12v power suply to the negative to the motor, its that ok ? there is another way to conect the power to the motor ?
Thank you very much, I wait for your advice.
Hello Eduard,
The current rating of the motor is very crucial normally the motor consumes slightly higher current than the rated current. And this might be the reason for your problem not for sure. So i suggest you to pick a transistor with higher current rating and substitute in the circuit instead of BD139 or you could go for motor Driving IC’s such as L293D. Here is a circuit which might help you with this Motor control using L293D.
Answering your 2nd question, motors doesn’t have fixed terminals i.e positive and negative. For a DC motor to work you must supply positive to one terminal and negative to another one. If you switch the supply terminals the motor will begin ti rotate in the opposite direction. That’s the reason for using DPDT switch in the circuit (to change direction of rotation) . I hope i answered your questions clearly.
If i want to use the L293D in this circuit where should i put the GND pin of this? at the GND or at the colector of the BD?
Chuado,
You intend to replace transistor with L293D chip?
saatana paskakytkentä homo!!!!!!!
Sorry Couldn’t get you, Kindly use English.