Concept of Increment and Decrement are used in almost every Embedded C program and its important to understand it deeply. This article was written in a view to help beginners to understand the Increment/Decrement concept of Embedded C. At the end of this tutorial you will be able to use increment/decrement concepts anywhere as well as alter it based on your design requirements.
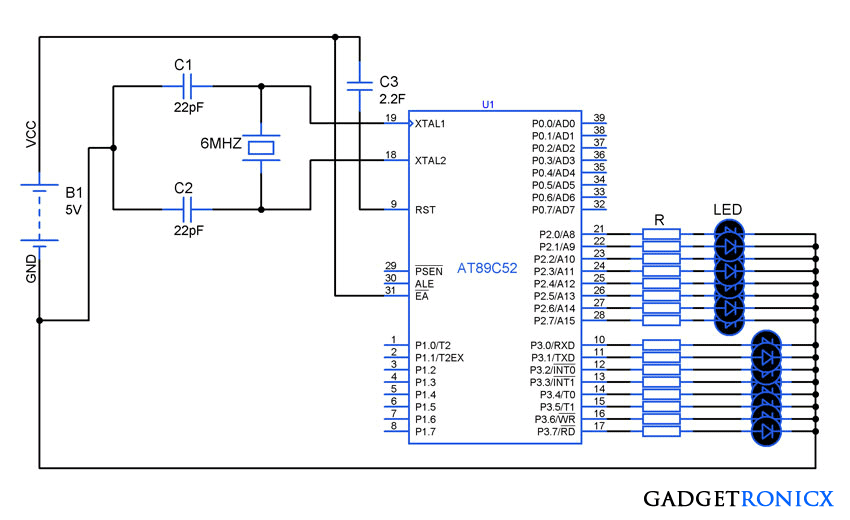
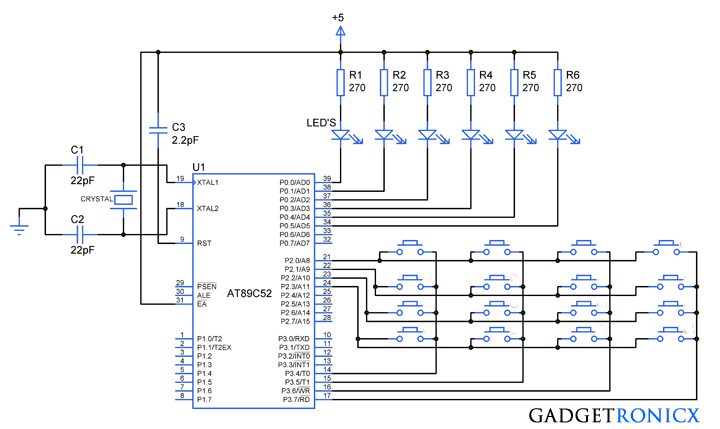
In this tutorial i have used AT89C52 microcontroller to demonstrate the working of these two concepts. In the above design you can see two sets of 8 LED’s connected to the port P2 and P3 of the 8051 Microcontroller. Here the program was coded in way to increment a specific value and the increment value was given through Port3. The LED was added to indicate the increment values in the port3. Meanwhile Port P2 was used here to give the inverse of the values obtained from Port P3.
TYPES OF INCREMENT/DECREMENT:
Generally there are two increment/decrement one is Pre increment and post increment. Pre increment represented by putting the ++/– sign before the variable like shown in the line 9 (++i) of the program. Whereas post increment/decrement denoted by i++. Both of these have differences and have purposes while implementing in a program. Let me explain with a example.
Consider two variables x and y, where the value of x is equal to 3 and y is 0. Take a look at the below statements and guess the results.
Seen the difference? Yes when you are doing a Pre increment/decrement a value it will be first incremented and then give the output to another operation. Whereas in post increment the current value was given as output to another operation and then incremented.Got the difference? Lets move into the program part.
INCREMENT PROGRAM:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<reg51.h>
unsigned char i; /*1Byte Variable Declaration*/
int j; /*2Byte Variable Declaration*/
void delay(void); /*Delay Function Declaration*/
void main()
{
i=0x00; /*Assigning Values to the variables*/
while(++i);
{
P3=i; /*LED's of port 3 will up count the integer value*/
P2=~i; /*LED of port 2 give the inverse of the value in P3*/
delay(); /*Delay function is called*/
}
while(1); /*Super Loop*/
}
void delay()
{
for(j=0;j<=15000;j++);
}
The first two lines was the inclusion of registry files and the 3,4 was assigning variables.We should use delay to view output since speed of the Microcontroller is very high.The i value was given as 0x00 which indicates that it was a hexadecimal number. Delay was used by calling the sub routine in the main program.
EXPLANATION:
The value of 00 equals 0000 0000 that is the combination of two 4 bit numbers given to the respective ports. The 00 value was loaded into the variable i in the line 8. While(++i) is a loop which keeps on incrementing the value of i and give it to the port 3 whereas inverse goes to the Port2.
The value of i starts incrementing from 0x00 and ends with 0xff in the port3 in the above program. While(1) is a super loop which is used to run the continuous loop and exit once the complete increment is over.
DECREMENT PROGRAM:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<reg51.h>
unsigned char i; /*1Byte Variable Declaration*/
int j; /*2Byte Variable Declaration*/
void delay(void); /*Delay Function Declaration*/
void main()
{
i=0xff; /*Assigning Values to the variables*/
while(--i);
{
P3=i; /*LED's of port 3 will down count the integer value*/
P2=~i; /*LED of port 2 give the inverse of the value in P3*/
delay(); /*Delay function is called*/
}
while(1); /*Super Loop*/
}
void delay()
{
for(j=0;j<=15000;j++);
}
I guess there is no need of much explanation here because there is only one major difference in between these programs. In the decrement program the initial value of i is 0xff that is 1111 1111 and it is gradually decremented to 0x00 by the end of the program. Here also while(1) was used as super loop and exits it once the decrement is fully over.